How have ICT-driven practices contributed to the COVID-19 pandemic response?
The Broadband Commission Working Group on Epidemic Management was organized to analyze international efforts, best practices, and lessons learned from the use of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs) in response to COVID-19, and to present collaborative approaches to overcome future pandemics. Launched in September 2020 and chaired by Dr. Hyeonmo Ku, Chief Executive Officer of the KT Corporation, the Working Group produced a 2021 research report to study the global framework for various pandemic management information communication technology (ICT) strategies, to alleviate humanitarian and social loss in the future.
Setting the Stage
Background Overview
In the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, the whole world exerted immense efforts to overcome the virus. While governments and medical sectors concentrated on treatment and development of vaccines and medicines, the ICT sector played a pivotal role in enabling the continuation of various economic activities while helping alleviate the spread of the virus through data collection and digital communication.
What are NPIs?
Non-pharmaceutical interventions, or NPIs, are public health measures designed to control the spread of infectious diseases without the use of pharmaceutical drugs. They include a range of recommendations from the individual level (e.g. hygiene, hand-washing and mask-wearing) to the societal level (e.g. social distancing, school closures, social gathering restrictions and lockdowns). NPIs also involve such measures as quarantines, isolation of confirmed cases, testing and contact tracing, and regular cleaning of public spaces using specific protocols.
How have ICTs been used in NPIs during the COVID-19 outbreak?
NPIs adopted since March 2020, when COVID-19 was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO), varied across countries and regions but many involved the use of information and communications technologies. The areas where ICT contributions are key include: digital epidemiological surveillance (using AI and other tools); medical image analysis and screening candidates for vaccines and treatment; symptom questionnaires through apps or other digital data-collection approaches; data extraction and visualization; contact tracing through mobile phone records and Bluetooth data; public communication through social networks; and telemedicine.
The Way Forward
Findings and Recommendations
The research report of the Working Group on Epidemic Management, Importance of ICT and Global Cooperation for Future Epidemic Management, examines the NPIs undertaken by countries to control the spread of COVID-19. In particular, it looks into 14 countries selected as comparative examples of both developed and developing countries in the Asian, European, North American, and African regions.
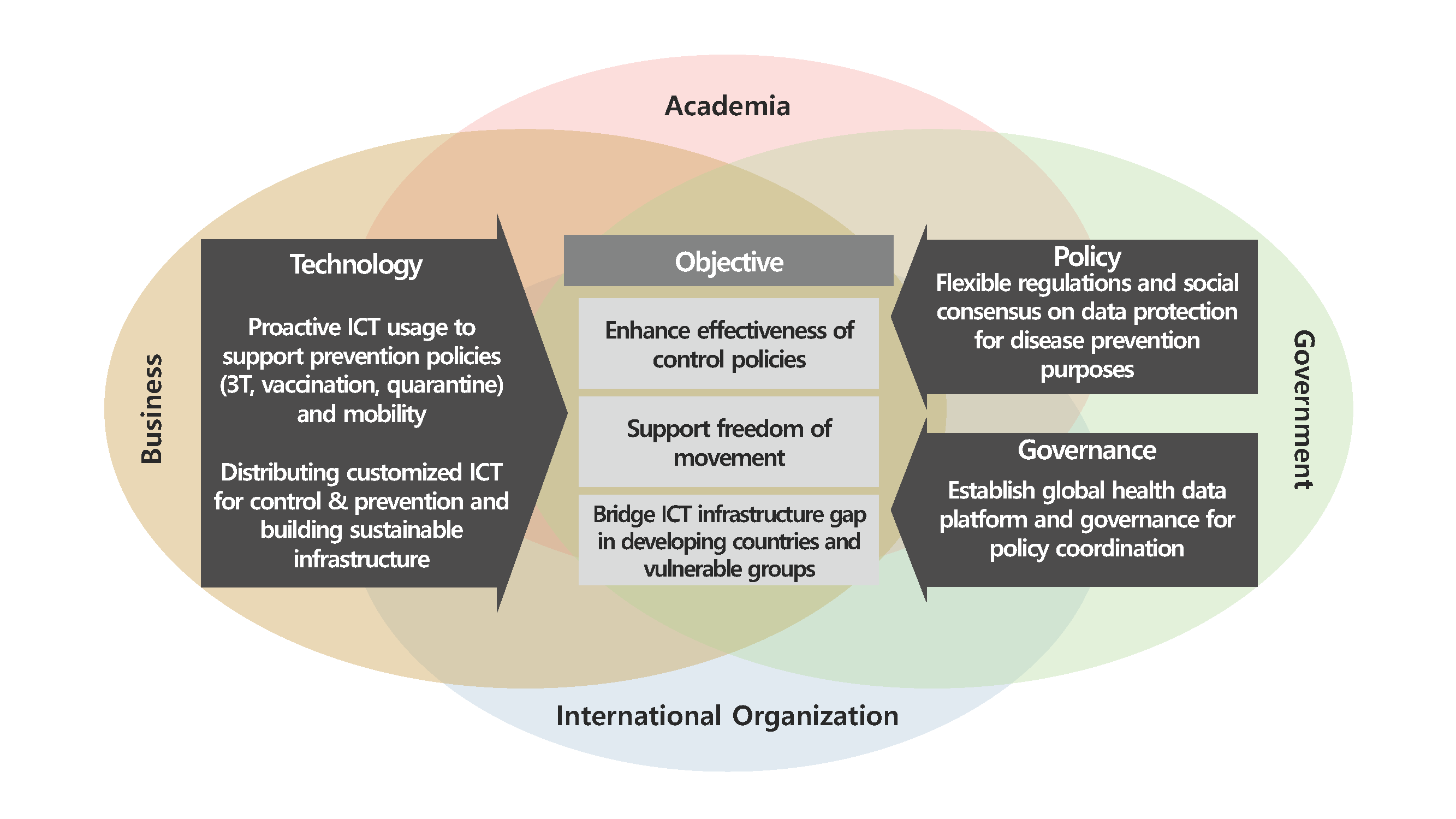
Drawing lessons through the review of national response policies and outcomes, the paper offers four considerations, all of which should be founded on the specific context of individual societies and communities, and take into consideration people’s level of access to, and capacity to use, ICTs (including the public as well as those involved in any public health response).
1.
Timely ICT-based responses require up-to-date and accurate data, and the development as well as deployment of strategies and tools for data collection. The use and management of data need to be guided by appropriate policy and regulatory frameworks that guarantee personal privacy and data security.
2.
Investment should be made to expand the role of ICT in public health, particularly in the context of a crisis.
3.
We need to bridge the ICT infrastructure gap between countries to help the disadvantaged
4.
A global public-private governance for data sharing and policy coordination should be built
Download the research report to read all of the Working Group’s proposed considerations.
- Preemptive consideration is necessary to ensure pandemic preparedness through new response systems and action plans. Proactive deployment of ICTs in particular will be a key factor in building a successful response system.
Considerations for a future epidemic response
The Working Group Model
Composition and Activities
Dr. Hyeonmo Ku
Chief Executive Officer, KT Corporation
Co-Chairs: Dr. Hyeonmo Ku
- President Paul Kagame, Government of Rwanda
- ITU
- Carlos Jarque, America Movil
- Mats Granryd, GSMA
- Makhtar Diop, IFC
- Baroness Beeban Kidron
- Sun Yafang, Huawei
- Achim Steiner, UNDP
- Government of South Africa
- Dr. Hessa Al Jaber, Eshailsat
- Leong Keng Thai, Singapore
- Robert Kirkpatrick, UN Global Pulse
- Dato Lee Yee Cheong, ISTIC
- Jacob Lee, Hallym University
- Joanna Rubinstein, World Childhood Foundation
In continuation of the work of Working Group on Epidemic Preparedness in 2018, the new Working Group on “Epidemic Management” was proposed to analyze various global efforts, best practices and valuable learnings to tackle COVID-19 Pandemic and present how the world could work together to overcome another wave of epidemics and pandemics, reflecting various social, cultural and national environment and approaches. The Group was launched in September 2020 during the Broadband Commission’s Annual Fall meeting.
Focus Area
Outcome Resources
Co-Chairs
Dr. Hyeonmo Ku
Chief Executive Officer, KT Corporation
Broadband Advocacy Targets
SDGs







